This quickstart uses Claude Desktop, but it also works with other MCP clients, like Cursor and Claude Code.
Steps
Setup Scorecard account
Create a Scorecard account if you don’t have one already.
Install the Scorecard MCP server in Claude
Open Claude and add the Scorecard MCP server using the remote configuration:Once connected, Claude will have access to all Scorecard API capabilities through natural language.
- Open Claude settings
- Navigate to the “MCP Servers” section
- Add a new remote server with URL:
https://mcp.scorecard.io/mcp - Complete the OAuth authentication flow to connect your Scorecard account
The remote MCP server requires no local dependencies or API key management. Authentication happens securely through your browser.
Create a project
Simply ask Claude to create a new Scorecard project:

Create a new Scorecard project called “Customer Support Bot Evaluation” for testing my AI customer support assistant.


Claude will automatically use the appropriate MCP tools (like
create_projects, list_projects) based on your natural language request.Create a testset with testcases
Now create a testset to hold your evaluation test cases. Describe the structure you need: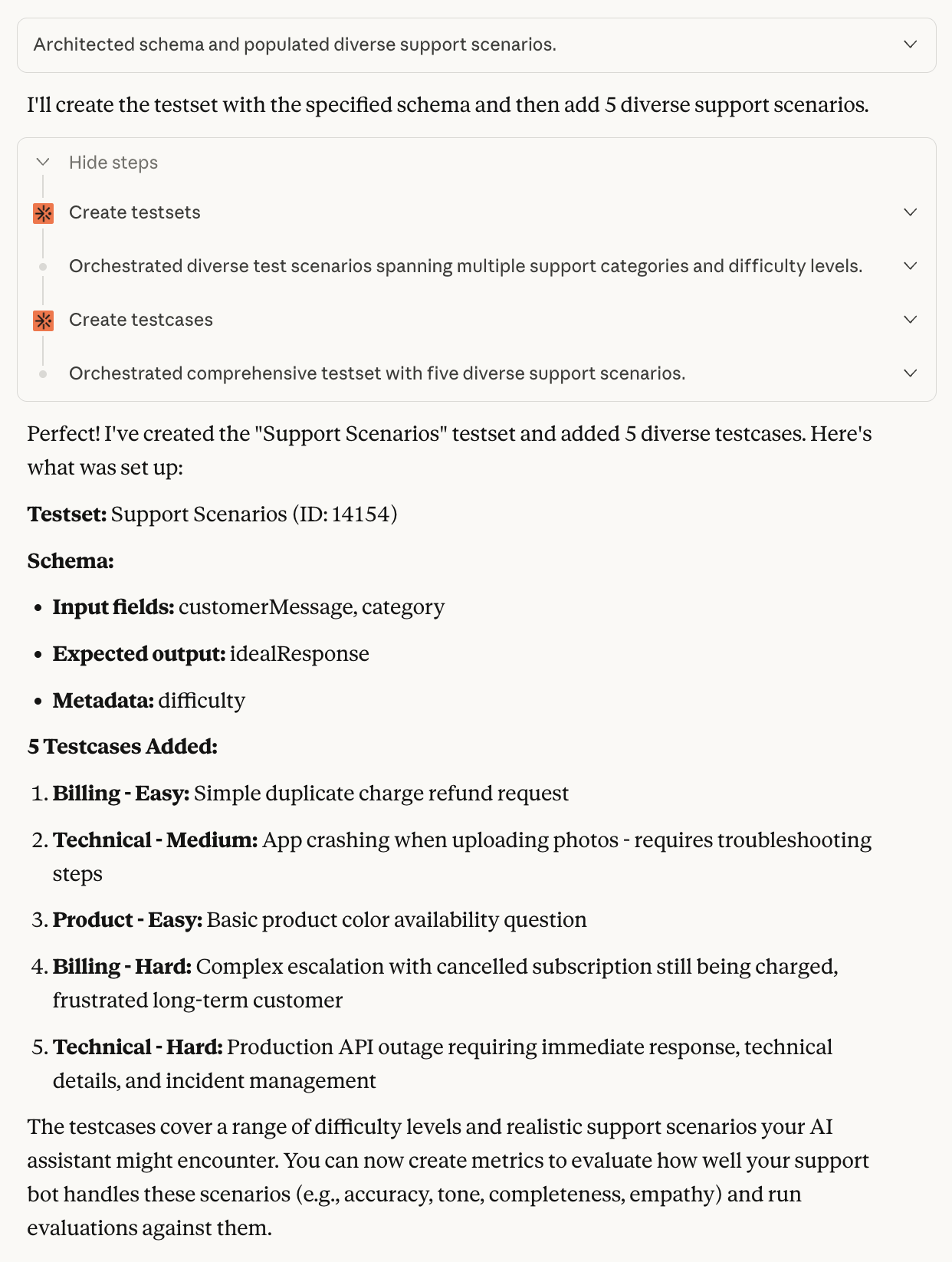
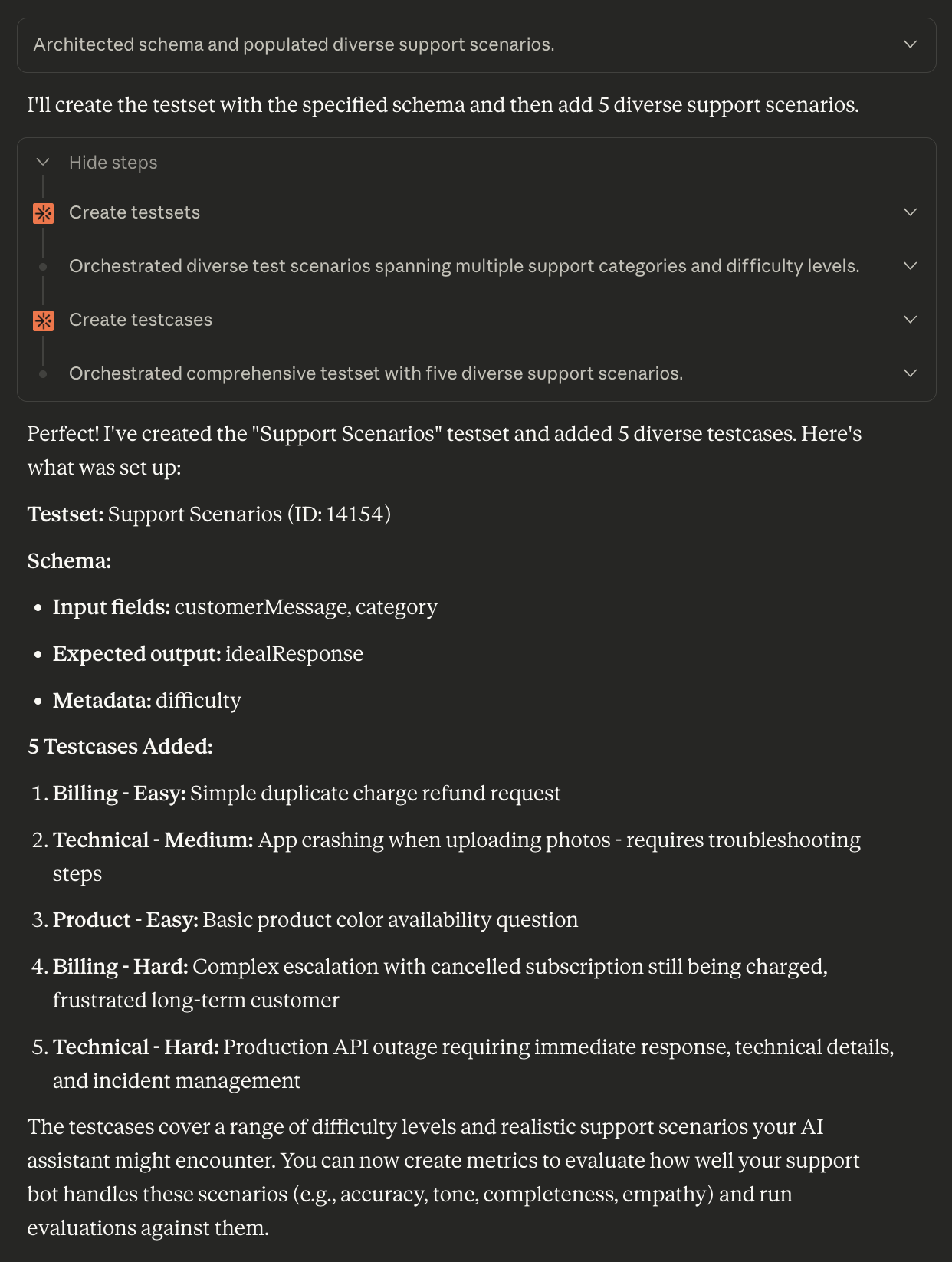
Create a testset called “Support Scenarios” in this project. The testcases should have:Then add 5 testcases covering different support scenarios.
- Input fields: “customerMessage” (the customer’s question) and “category” (support category like billing, technical, or product)
- Expected output field: “idealResponse” (what a great response from the agent looks like)
- Metadata field: “difficulty” (easy, medium, or hard)


Create evaluation metrics
Define metrics to evaluate your AI system. Describe what “good” looks like: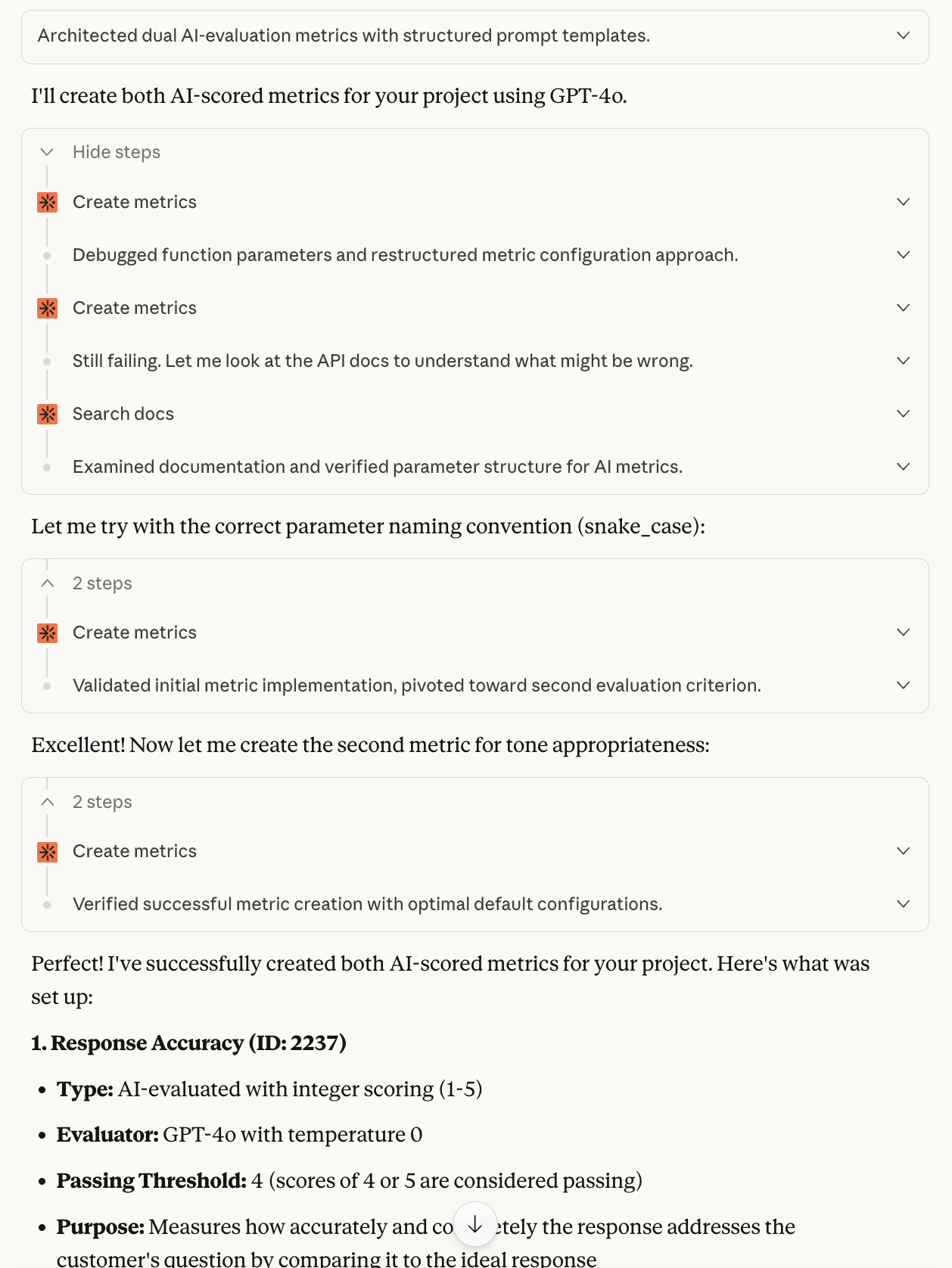
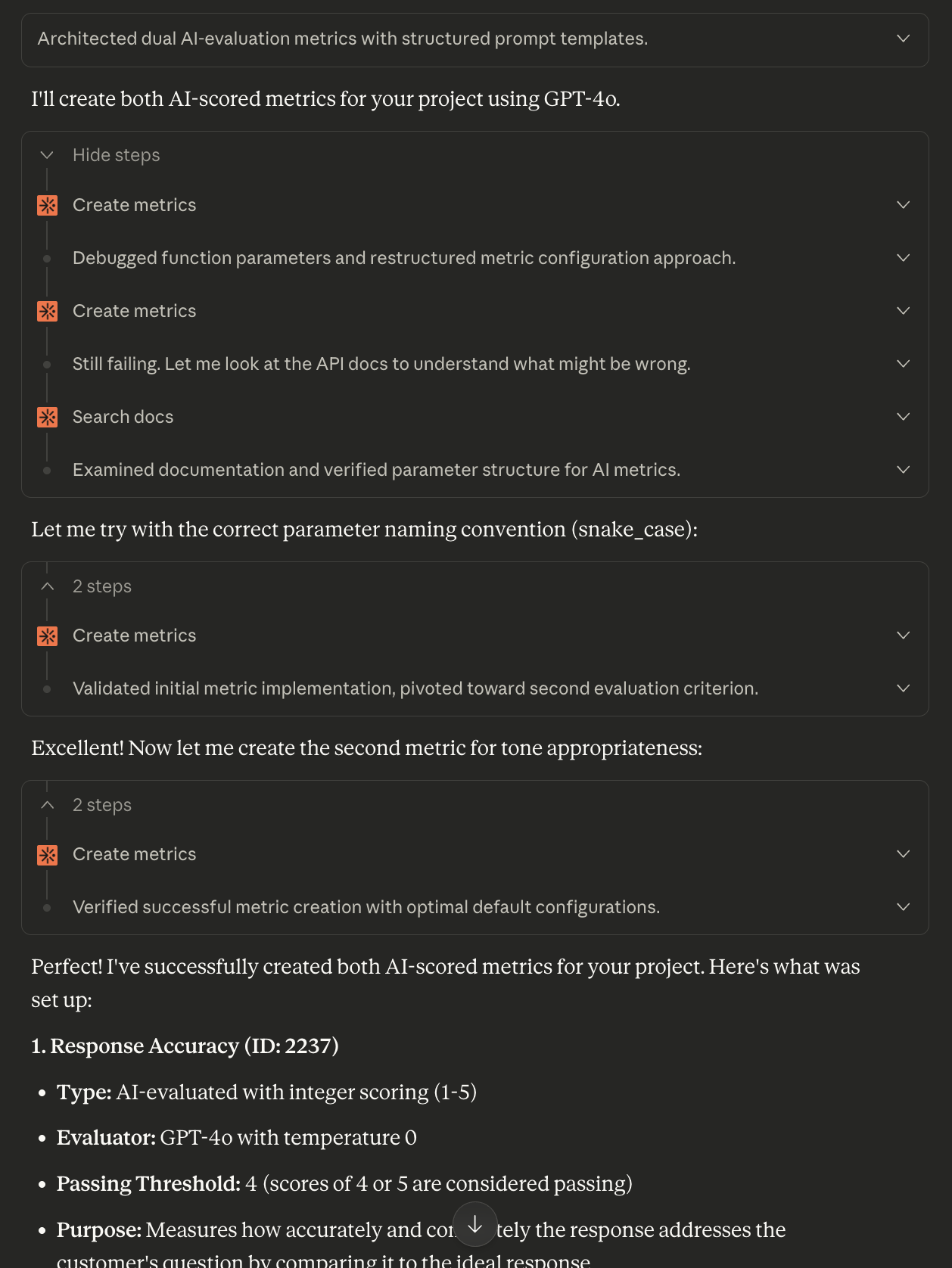
Create two AI-scored metrics for this project:Use GPT-4o as the evaluator with temperature 0 for consistency.
- “Response Accuracy” (integer) - Measures how well the response answers the customer’s question compared to the ideal response
- “Tone Appropriateness” (boolean) - Checks if the response uses professional, empathetic language appropriate for customer support


Claude’s initial tool call to
create_metrics failed because it used the wrong arguments, but it was able to eventually succeed by reading the documentation and trying again.View your setup in Scorecard
Open your Scorecard project in the web UI to see everything that was created!Everything is now ready to score records. You can score records against your metrics through the UI, SDK, or continue using Claude with MCP.
Next: Score records
You can score records from the Records page, the SDK, or the Scorecard playground.You can also continue the conversation to analyze and iterate on your metrics and scores.
Explain the latest scoring results for this project.
Update the Response Accuracy metric to be stricter about factual details.
Add 5 more testcases covering edge cases like angry customers and off-topic questions.The MCP server gives Claude access to the full Scorecard API, so you can manage your entire evaluation workflow conversationally.
Tips for Using the MCP Server
Troubleshooting
I have a different MCP client.
I have a different MCP client.
The Scorecard MCP server works with most MCP clients, including Claude Desktop, Cursor, and Claude Code. Make sure you’ve added the remote server URL correctly (
https://mcp.scorecard.io/mcp) and completed the OAuth flow. See the MCP Server documentation for more installation instructions.MCP server does not show up in Claude.
MCP server does not show up in Claude.
Make sure you’ve added the remote server URL correctly (
https://mcp.scorecard.io/mcp) and completed the OAuth flow. Restart Claude if needed.Claude shows an authentication error.
Claude shows an authentication error.
The MCP server uses OAuth tokens that may expire. Try disconnecting and reconnecting the MCP server in Claude settings to refresh authentication.
Claude says it can't find MCP tools.
Claude says it can't find MCP tools.
Verify the MCP server is connected and enabled in Claude settings. You should see “Scorecard” listed in your active MCP servers.
I can't connect to remote MCP servers.
I can't connect to remote MCP servers.
For local installation with your Scorecard API key, see the MCP Server documentation. Use
npx -y scorecard-ai-mcp@latest with environment variables.Learn More
Ready to go deeper? Check out these resources:MCP Server Features
Complete guide to the Scorecard MCP server capabilities and architecture
Metrics Guide
Deep dive into creating and managing evaluation metrics
Testsets
Learn about testset schemas, field mappings, and organization