Overview
Scorecard’s MCP (Model Context Protocol) server transforms AI assistants like Claude and Cursor into conversational AI evaluation companions. With natural language commands, you can manage projects, create testsets, configure metrics, run evaluations, and analyze results—all through your favorite AI assistant’s interface.Setting Up the MCP Server
Prerequisites
- An MCP-compatible client (Claude Desktop, Cursor, or other MCP clients)
- A Scorecard account with API access
Remote configuration (recommended)
You can install the Scorecard remote MCP server without any dependencies.Claude Desktop
Go to Claude Desktop settings page and click on the “Connectors” tab. Click “Add custom connector” and paste the following URL:https://mcp.scorecard.io/mcp. Click “Add” on the modal, then click “Connect” on the modal to login to Scorecard.
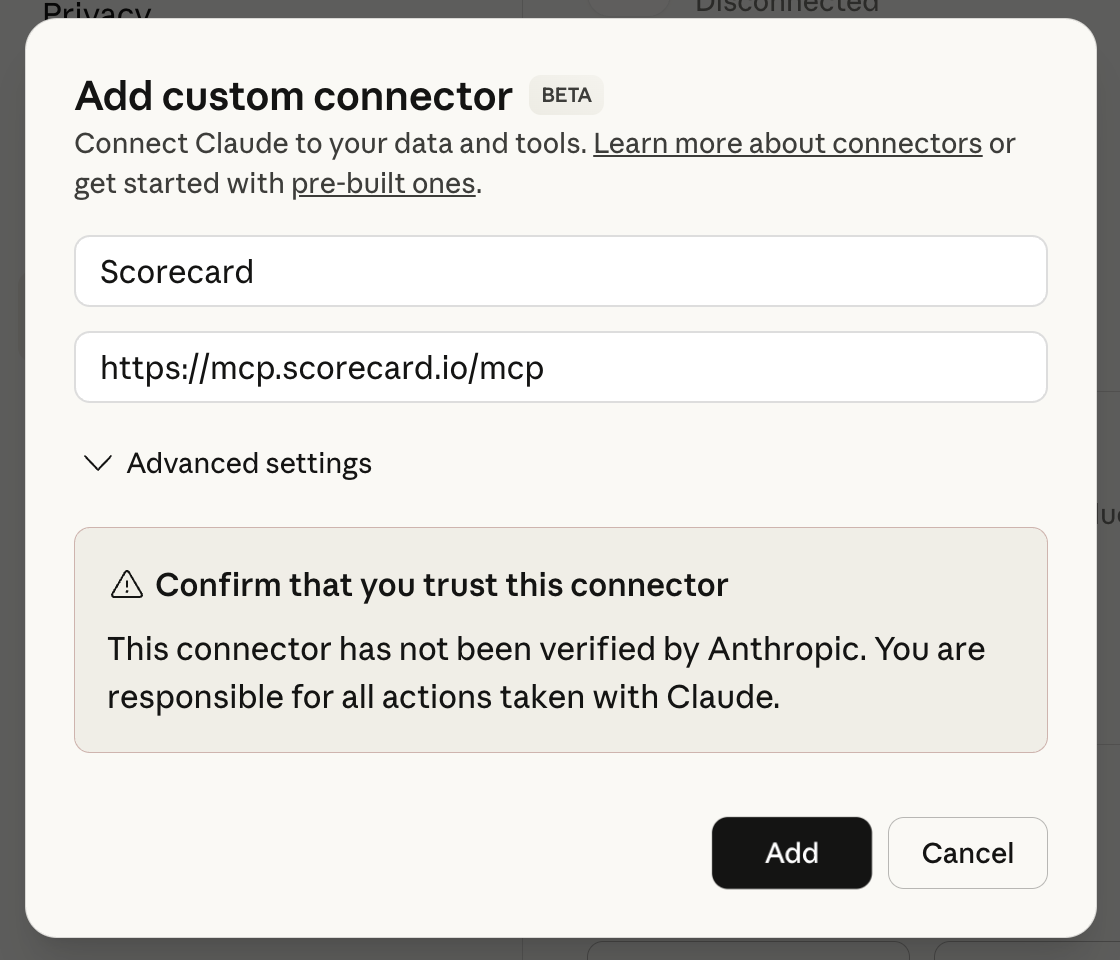
Local configuration
You can directly run the MCP Server locally via npx:The MCP server uses Clerk OAuth authentication and JWT tokens to securely connect to your Scorecard account. The configuration is identical across all MCP clients—simply add it to your client’s MCP settings.
Core Capabilities
The MCP server provides natural language access to Scorecard’s core functionality:Project Management
Project Management
Create and manage evaluation projects for your AI systems.Example Commands:
- “Create a new project for evaluating my customer service chatbot”
- “Show me all my current projects”
- “Set up a project for testing my RAG pipeline”
Testset Creation
Testset Creation
Build comprehensive testsets with various scenarios and edge cases.Example Commands:
- “Create a testset for customer service scenarios”
- “Add 20 testcases covering product returns and refunds”
- “Import testcases from my CSV file”
Testcase Organization
Testcase Organization
Organize and categorize your testcases for systematic evaluation.Example Commands:
- “Group testcases by difficulty level”
- “Add tags for ‘edge cases’ and ‘common queries’”
- “Show me all testcases related to billing issues”
Custom Metrics Configuration
Custom Metrics Configuration
Define metrics that matter for your specific use case.Example Commands:
- “Configure accuracy and helpfulness metrics”
- “Add a custom metric for response relevance”
- “Set up hallucination detection scoring”
AI System Version Management
AI System Version Management
Track different versions of your AI systems and models.Example Commands:
- “Register my GPT-4 based assistant as version 1.0”
- “Create a new version for my updated prompt template”
- “Compare versions 1.0 and 2.0 of my chatbot”
Evaluation Runs & Analysis
Evaluation Runs & Analysis
Execute evaluations and analyze performance results.Example Commands:
- “Run an evaluation against my latest model”
- “Show me the performance results from yesterday’s run”
- “Compare accuracy across the last 5 evaluation runs”
Example Workflows
Complete Evaluation Setup
Here’s how you might set up a complete evaluation workflow using natural language in any MCP client:Create a Project
“Create a new project called ‘Customer Support Bot v2’ for evaluating my updated support assistant”
Define Testcases
“Create a testset with 50 diverse customer support scenarios including billing, technical issues, and product inquiries”
Configure Metrics
“Set up metrics for accuracy, response helpfulness, hallucination rate, and response time”
Continuous Testing Workflow
- Daily Testing
- A/B Testing
- Regression Testing
Example Commands:
- “Run daily evaluation on production model”
- “Alert me if accuracy drops below 85%”
- “Generate weekly performance report”
Advanced Use Cases
Multi-Model Comparison
Use your AI assistant to orchestrate complex multi-model evaluations: Example Commands:- “Compare GPT-4, Claude 3, and Llama 3 on my customer service testset”
- “Evaluate cost-performance tradeoffs between models”
- “Recommend the best model for my use case”
Automated Test Generation
Leverage your AI assistant’s understanding to create comprehensive test suites: Example Commands:- “Generate 100 edge cases for my medical diagnosis assistant”
- “Create adversarial testcases to test robustness”
- “Build a testset from real user conversations”
Performance Optimization
Get insights and recommendations for improving your AI systems: Example Commands:- “Analyze failure patterns in my evaluation results”
- “Suggest prompt improvements based on errors”
- “Identify which types of queries need more training data”
Technical Architecture
The MCP server is:- Built on the Model Context Protocol standard
- Compatible with any MCP client (Claude Desktop, Cursor, and more)
- Deployed on Vercel edge infrastructure for low latency
- Secured with Clerk OAuth authentication
- Open source and available on GitHub
Getting Help
If you encounter issues or have questions about the MCP server:- Check the GitHub repository for documentation
- Open an issue for bugs or feature requests
- Contact Scorecard support (support@scorecard.io) for account-related questions