Metrics serve as benchmarks for assessing the quality of LLM responses, while scoring is the process of applying these metrics to generate actionable insights about your LLM application.
Assess Your LLM Quality With Scorecard’s Metrics
Scorecard’s metric system is organized into three main components:- Metrics: Individual evaluation criteria that assess specific aspects of your LLM’s performance
- Metric Groups: Collections of related metrics for comprehensive evaluation
- Templates: Pre-built metric configurations you can copy and customize
Metric Templates
Our Scorecard Core Metrics represent industry-standard benchmarks for LLM performance, validated by our team of evaluation experts. Explore these templates on the Metrics page under “Templates”.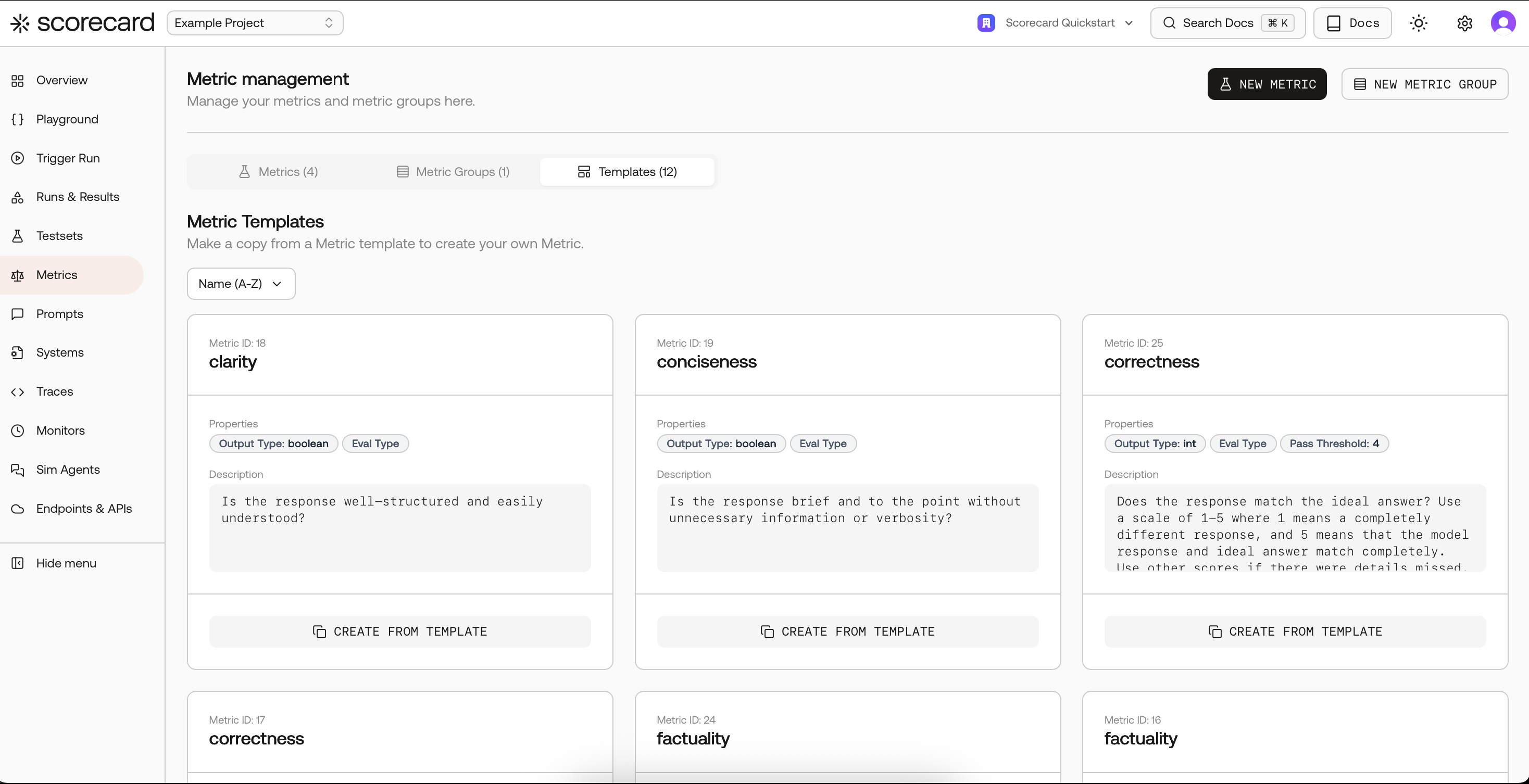
MLflow-Inspired Metrics
Scorecard provides support for MLflow-style metrics with additional capabilities like aggregation, A/B comparison, and iteration. Available metrics include:- Relevance: Evaluates how well the response aligns with the input and context
- Answer Relevance: Assesses relevance and applicability to the specific query
- Faithfulness: Measures factual consistency with provided context
- Answer Correctness: Evaluates accuracy against ground truth
- Answer Similarity: Assesses semantic similarity to expected responses
RAGAS-Inspired Metrics for RAG Pipelines
Scorecard provides RAGAS-style metrics for evaluating Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) systems: Component-Wise:- Faithfulness: Factual consistency with context
- Answer Relevancy: Pertinence to the prompt
- Context Recall: Retrieved context alignment with expected response
- Context Precision: Ranking of ground-truth relevant items
- Context Relevancy: Relevance of retrieved context to query
- Answer Semantic Similarity: Semantic resemblance to ground truth
- Answer Correctness: Accuracy compared to ground truth
Templates for common MLflow and RAGAS metrics are available under Templates. Copy a template (e.g., Relevance, Faithfulness) and tailor the guidelines to your domain.
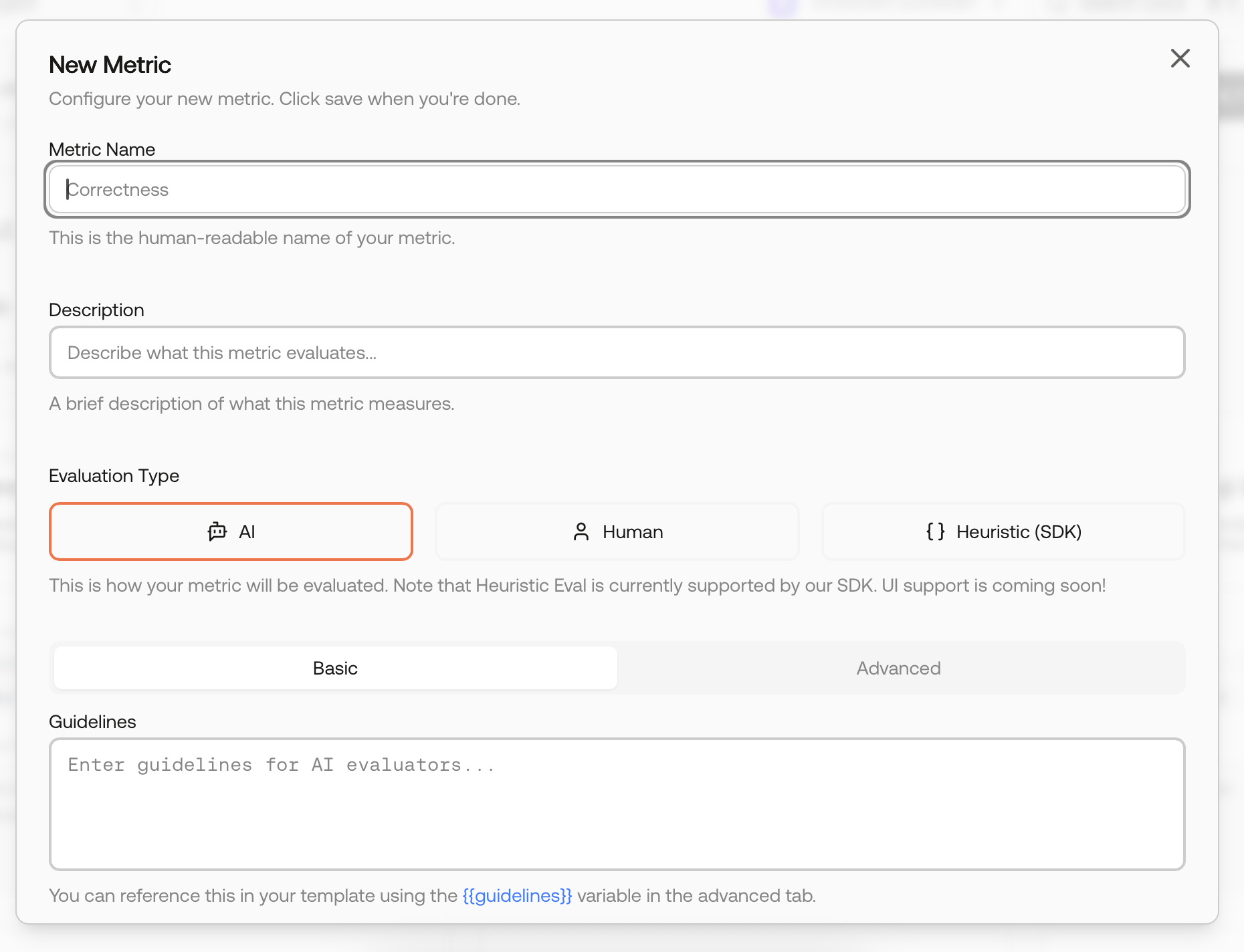
Define Custom Metrics for Your LLM Use Case
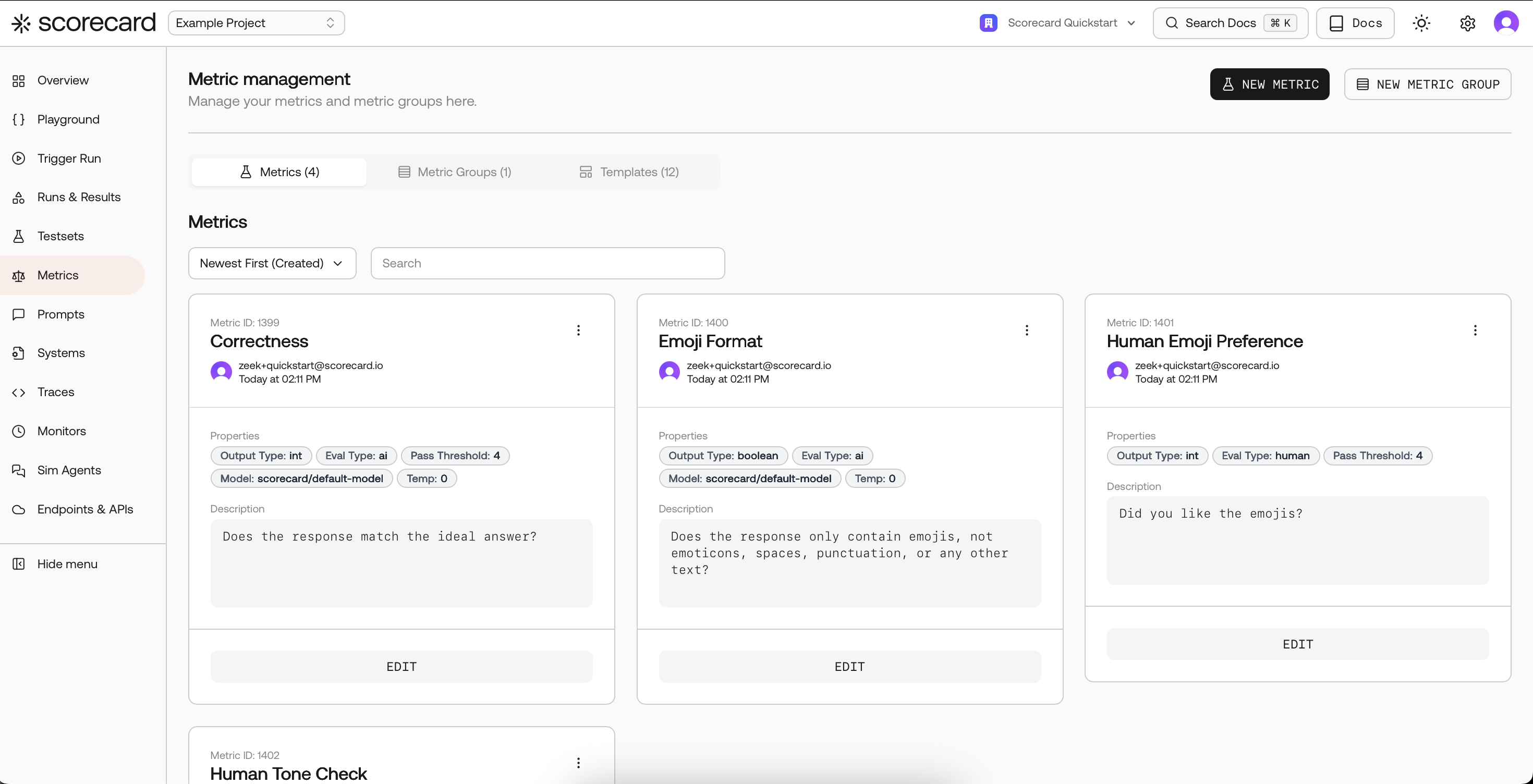
- Metric Name: Human-readable name
- Metric Guidelines: Natural language instructions for evaluation
- Evaluation Type:
- AI: Uses Metric Guidelines as prompt for an AI model
- Human: Manual evaluation by subject-matter experts
- Heuristic (Code): Custom Python or TypeScript logic (see Heuristic Metrics)
- Output Type: Boolean, Integer (1-5), or Float (0.0-1.0)
Output Types
Boolean Output Type
- Range: true/false
- Pass/Fail: Direct pass/fail representation
- Use cases: Format checks, refusals, policy/guardrails, presence/absence
- Aggregation: Pass ratios and counts
Integer Output Type
- Range: 1–5 (higher is better)
- Pass/Fail: Set a
passingThreshold(e.g., 4). Passes ifintScore ≥ threshold - Use cases: Rubric-based quality judgments (helpfulness, factuality, completeness)
- Aggregation: Means and distributions
Float Output Type
Normalized score between 0.0 and 1.0 for graded, continuous measurement.- Range: 0.0–1.0 (higher is better)
- Pass/Fail: Set a
passingThreshold(e.g., 0.90). Passes iffloatScore ≥ threshold - Use cases: Semantic similarity, confidence/uncertainty, coverage, quality scores
- Aggregation: Means for trend tracking
Automated Scoring
As testsets grow, manual evaluation becomes time-consuming. Subject-matter experts (SMEs) can become bottlenecks as the number of testcases increases. Scorecard’s AI-powered scoring automates evaluation, allowing SMEs to focus on complex edge cases while the system handles well-defined metrics.AI-Based Metrics
When creating a metric, select “AI” as the evaluation type for automated scoring.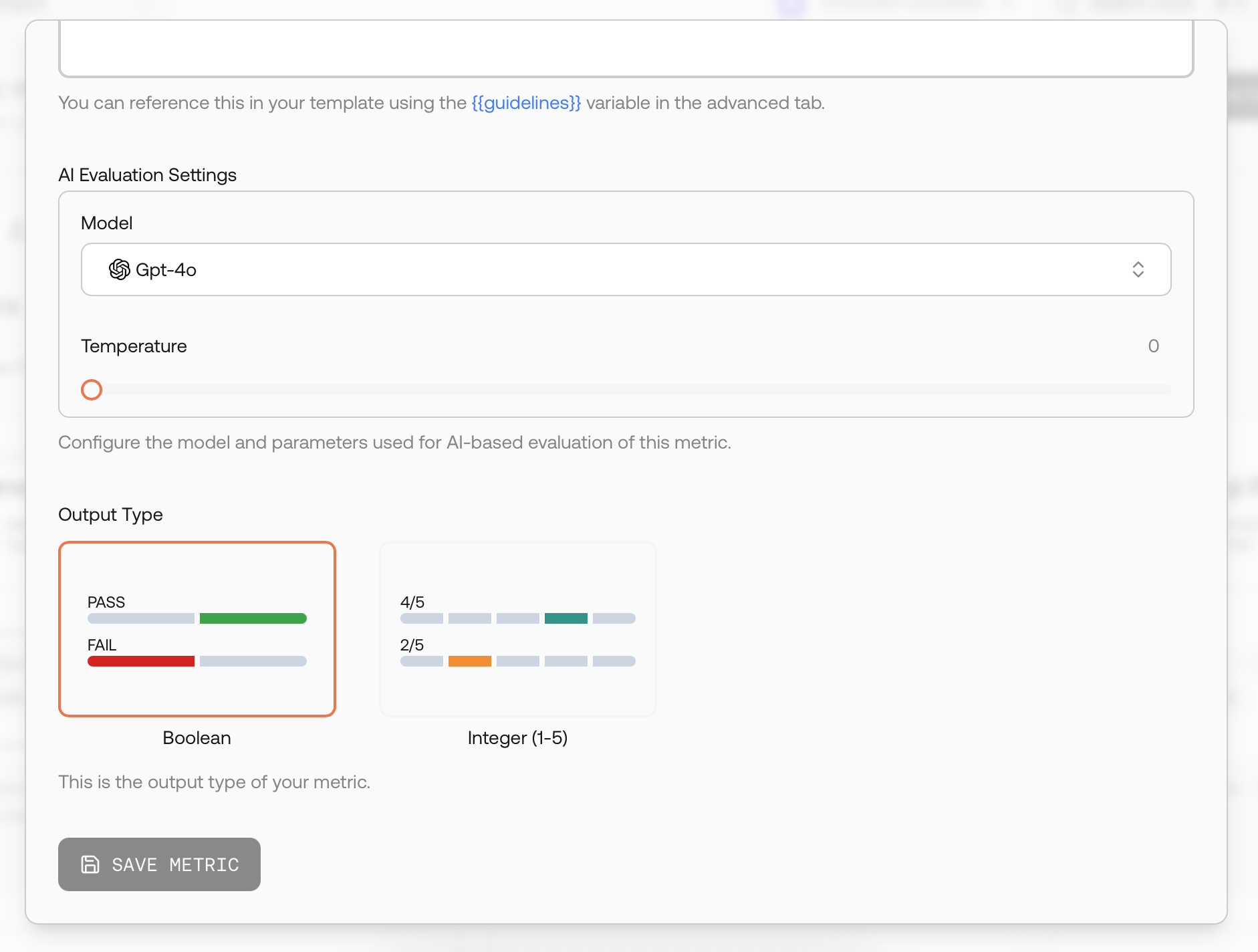
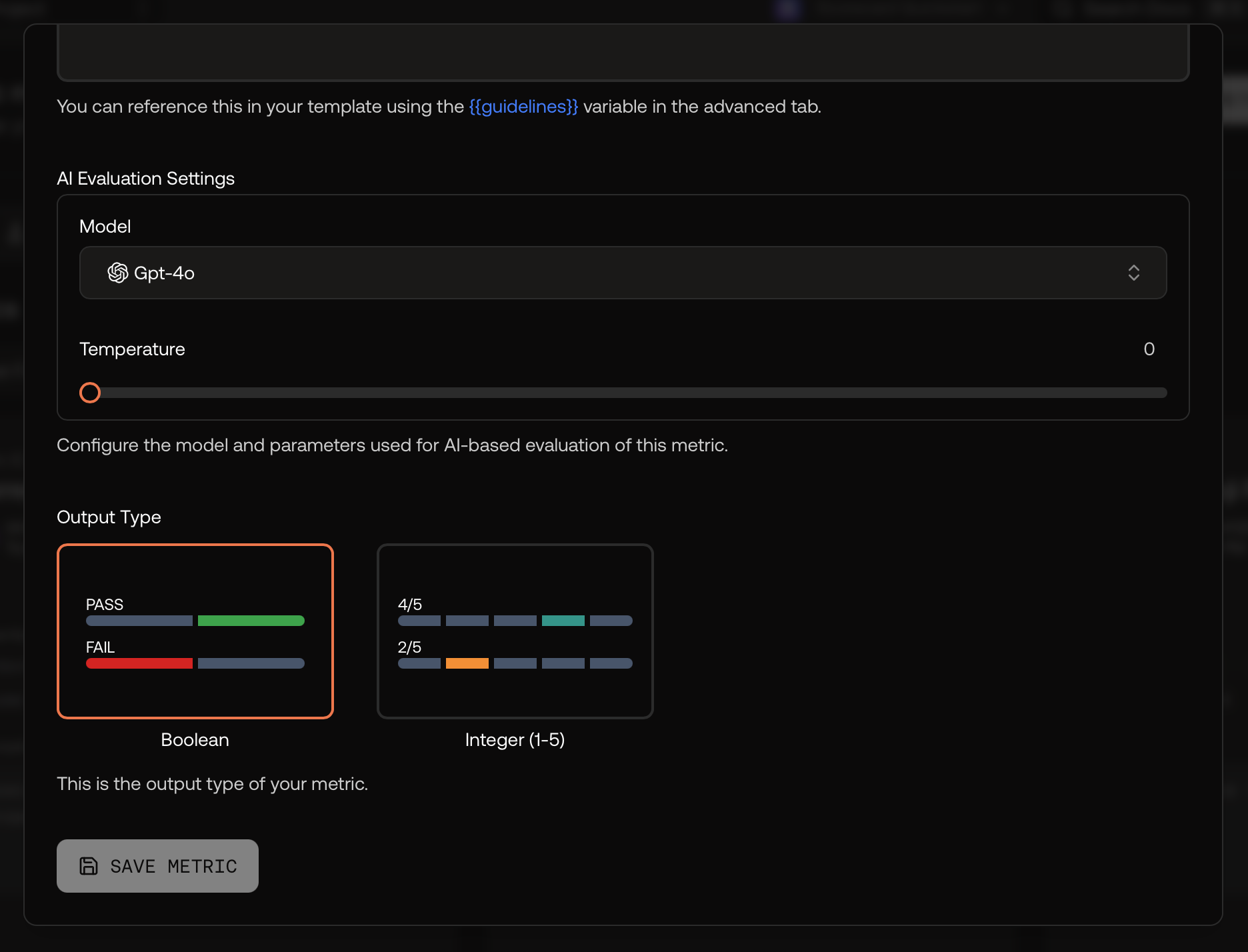
Configuration Modes
- Basic Mode: Define metric guidelines using natural language instructions
- Advanced Mode: Modify the full prompt template for sophisticated evaluation logic
Evaluation Settings
Configure AI evaluation parameters:- Model Selection: Choose models like GPT-4o
- Temperature: Control randomness (typically 0 for consistency)
- Additional Parameters: Model-specific settings
Automatic Scoring
When you score records (from the testset page, the Records page, or through GitHub Actions), AI and Heuristic metrics are evaluated automatically. You can view scoring progress and results on the Records page.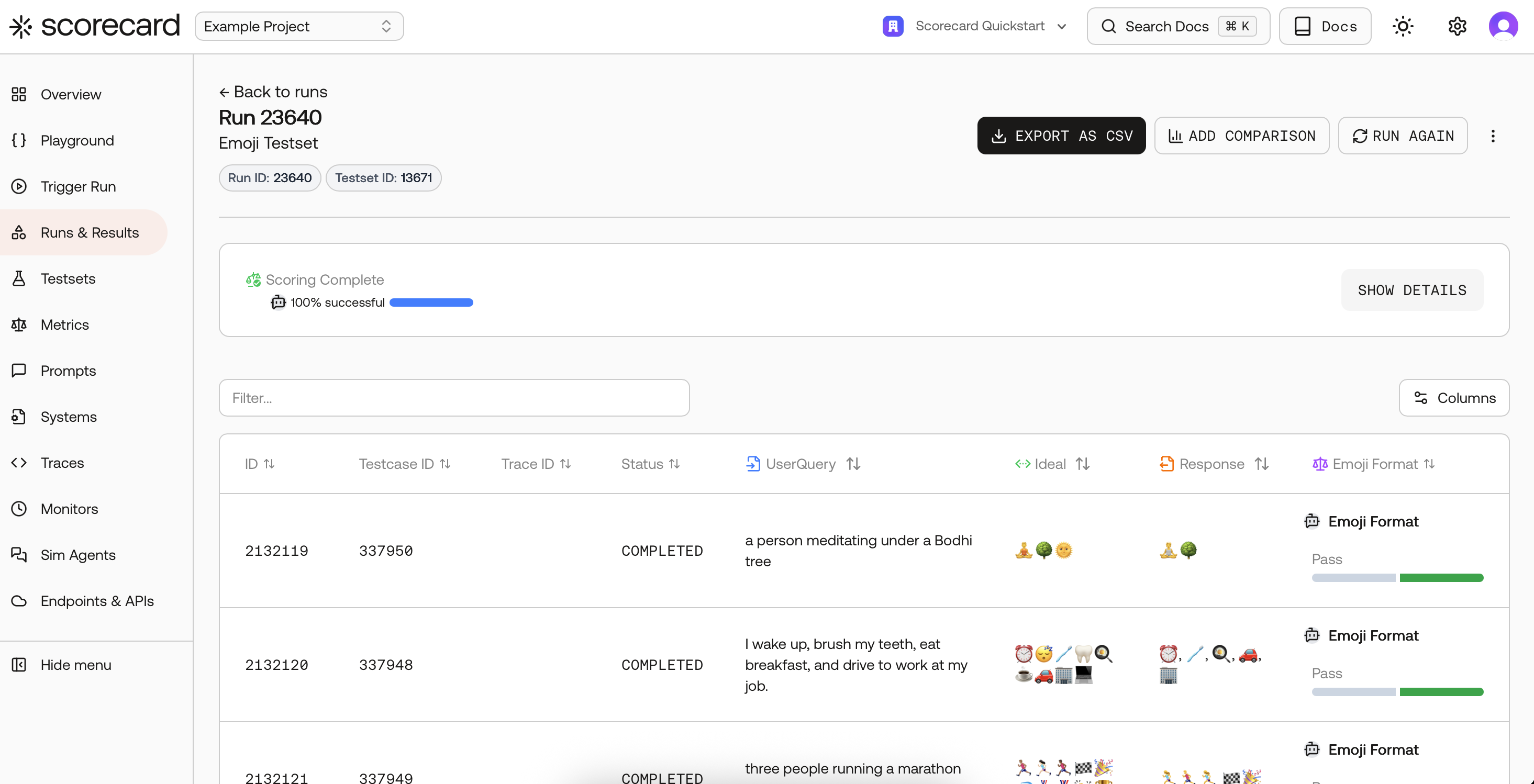
Score Explanations
Scorecard provides explanations for each score, helping you understand and validate the AI’s evaluation reasoning.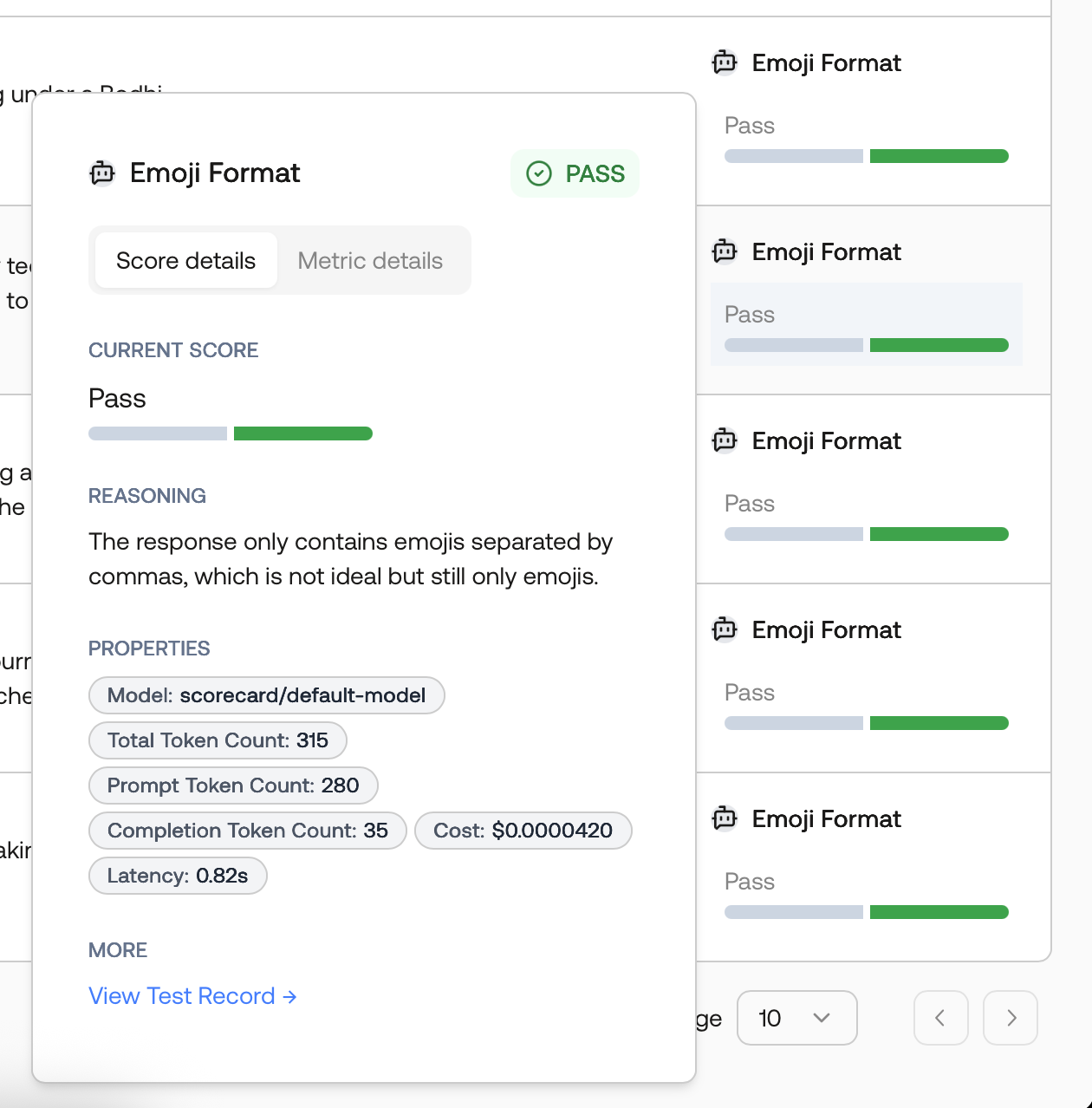
Heuristic Metrics (Code-Based Evaluation)
Write custom evaluation logic in Python or TypeScript for deterministic, rule-based scoring:- Checking for specific keywords or patterns
- Validating JSON structure or format
- Computing text similarity scores
- Measuring response length or complexity
- Custom business logic checks
Creating a Heuristic Metric
Select Heuristic as the evaluation type to access the code editor.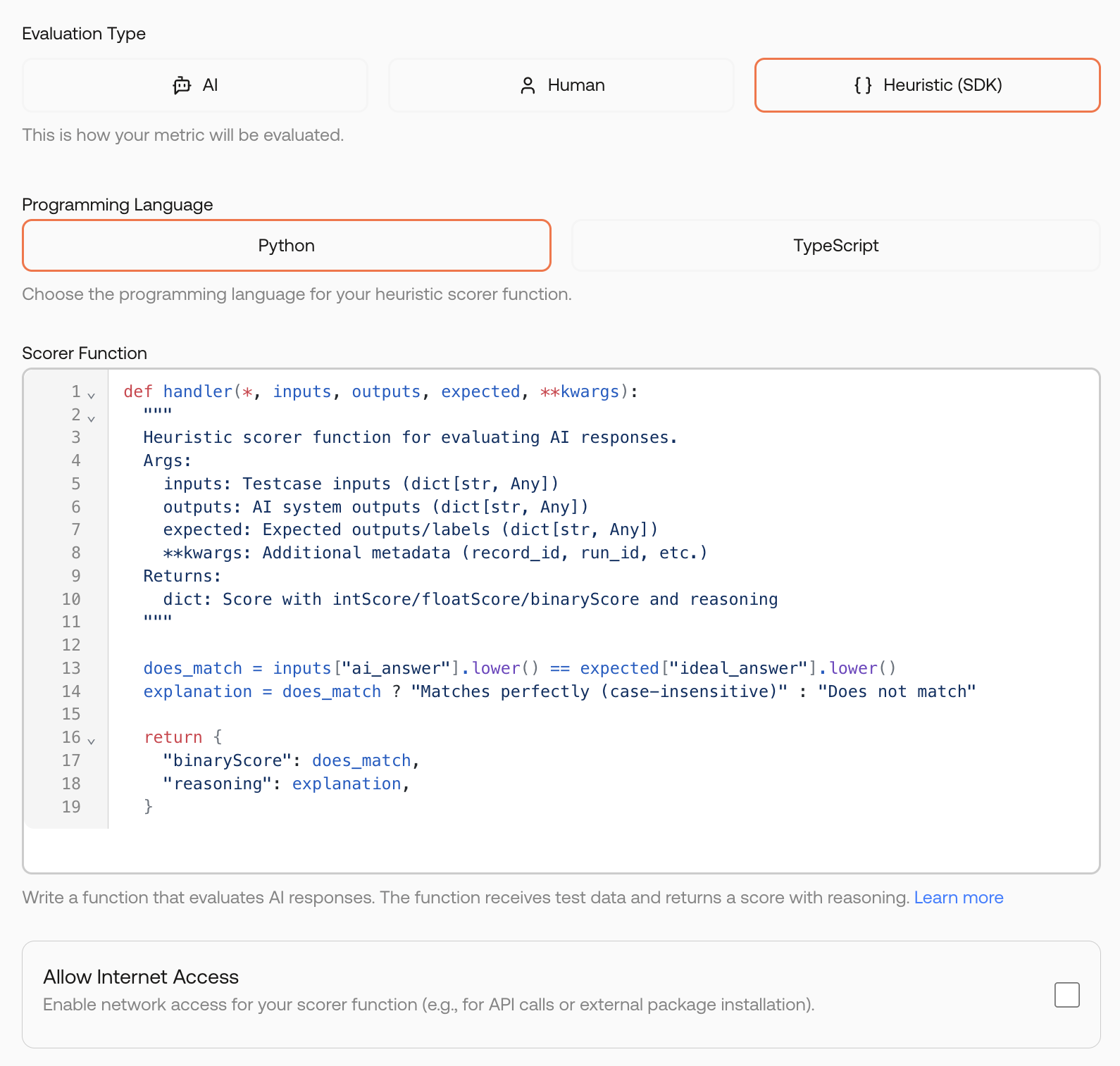
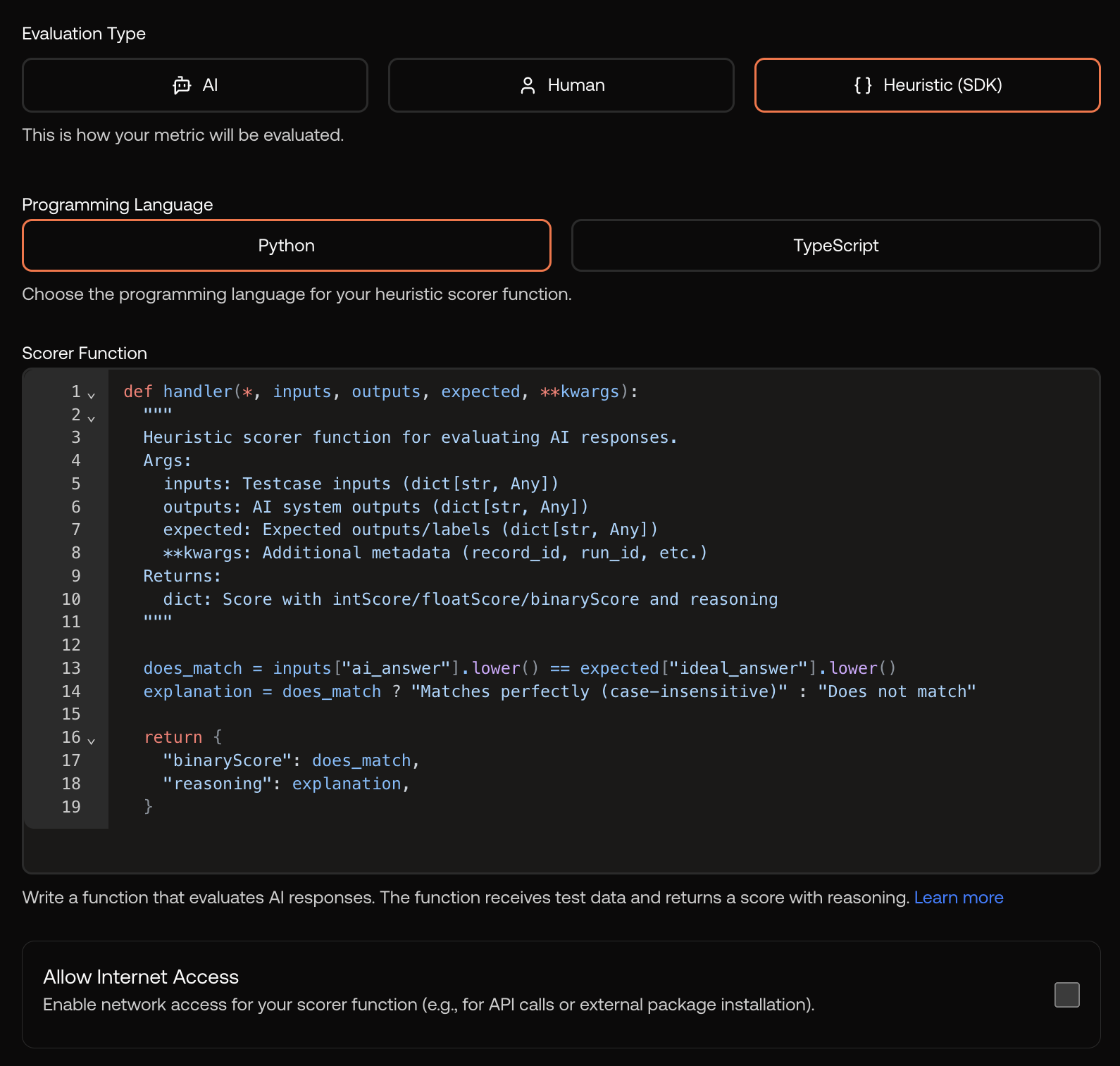
Writing Heuristic Code
Your code receives the record data and must return a score. Here’s the structure:- Python
- TypeScript
Secure Sandbox Execution
Code runs in a secure, isolated sandbox ensuring:- Safety: No external resource access
- Consistency: Deterministic results
- Performance: Optimized execution
The sandbox has limited access to external libraries. Common utilities like string manipulation and JSON parsing are available. Contact support if you need specific libraries for your use case.
Metric Groups
Group related metrics for consistent, repeatable evaluation. Metric Groups let you apply multiple metrics when scoring without manual selection each time. Create groups for specific use cases like RAG applications or translation tasks.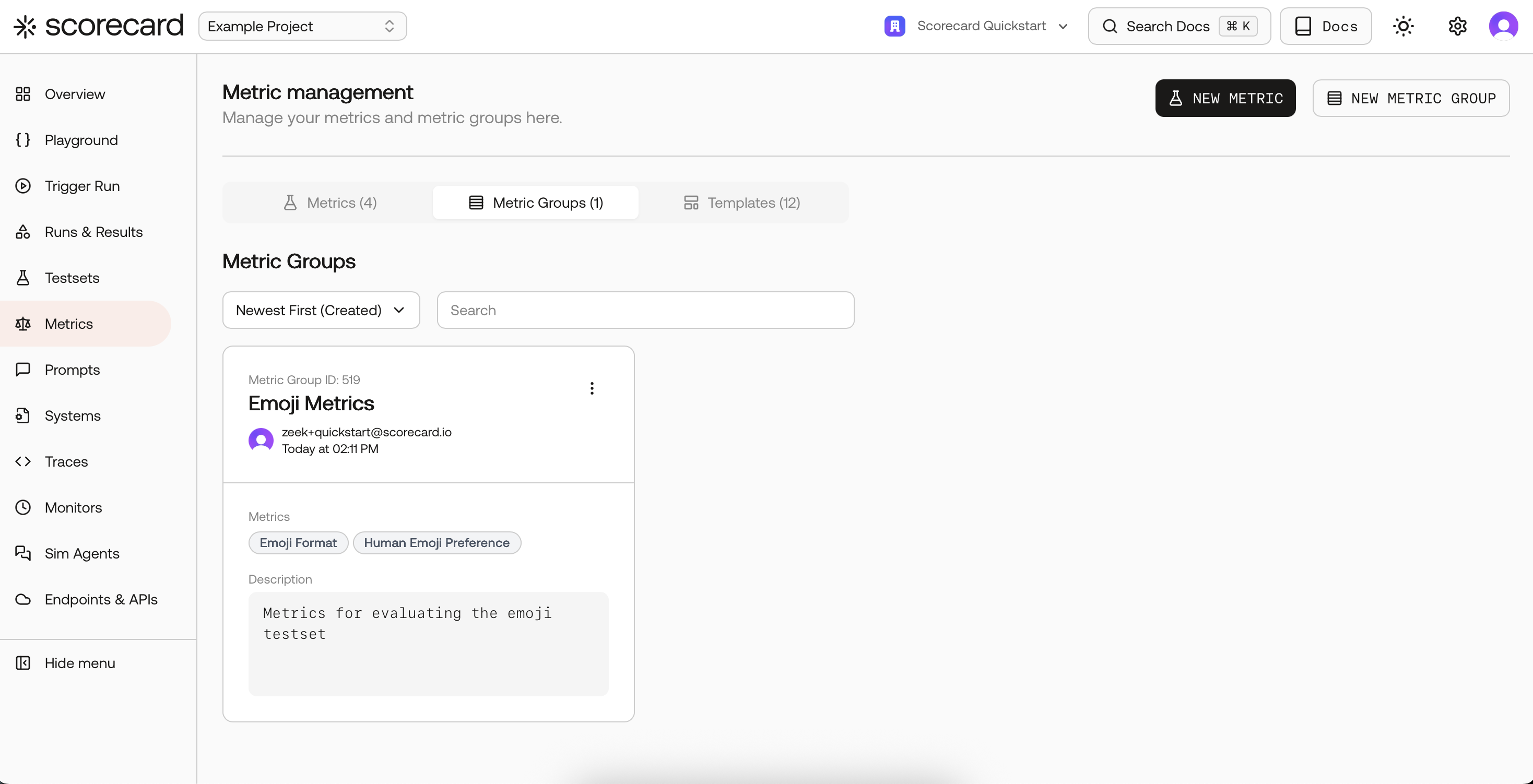
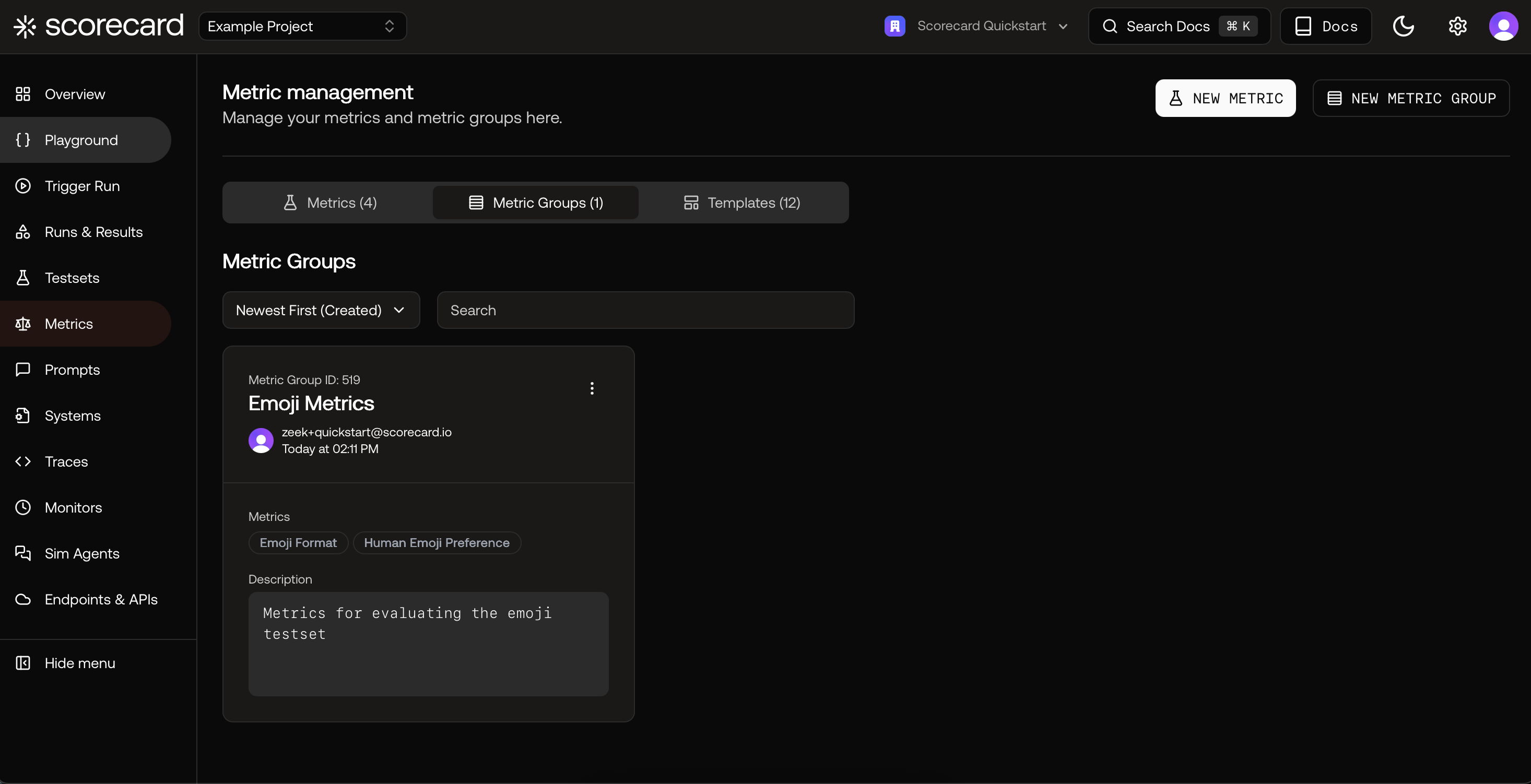
- Name: Human-readable identifier
- Description: Short summary of the group’s purpose